Region Branching
It is often the case that multiple whistles from different animals will overlap in time and frequency. If large groups of dolphins are encountered, then overlapping whistles tend to be the norm rather than the exception. While this may not be a problem if you are only interested in detecting whistles, if you are measuring bearings to individual whistles or if you are using the Whistle Classifier it is necessary to separate out the different sounds.
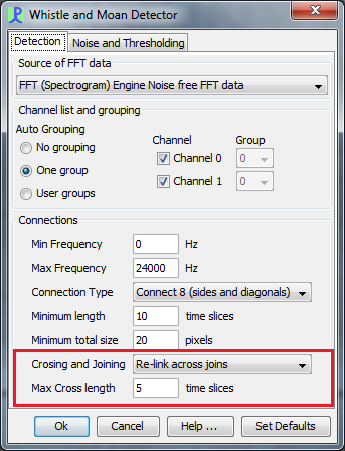
The Whistle and Moan detector has four options which control how overlapping whistles are handled
Leave branched regions intact
Discard branched regions
Separate all branches
Re-link across joins
This option is set at the bottom of the Whistle and Moan configuration dialog.
The different options are illustrated below using three simulated overlapping linear chirps.
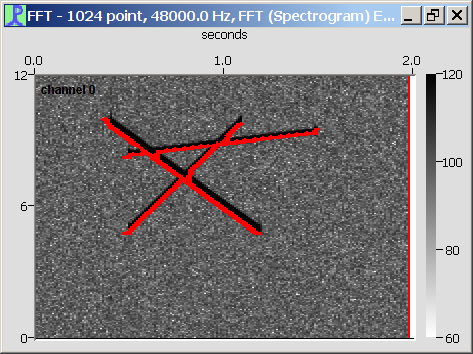
Leave branched regions intact
If this option is selected, then branched regions will be left intact and may contain more one actual sound.
Discard branched joins
If this option is selected, than any region that has more than one detected frequency peak in any time slice will be discarded.
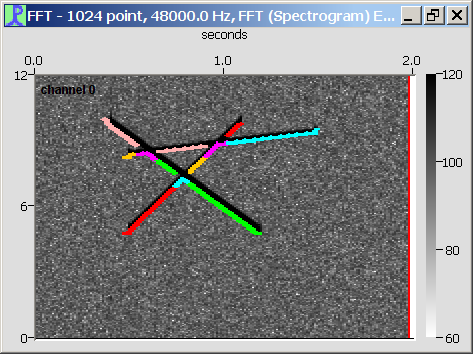
Separate all branches
If this option is selected, then all branches will be separated and passed on as individual sounds. A break is created every time the number of consecutive peaks changes. So a pair of crossing whistles will generally be broken into five parts - each of the four branches and the crossing point itself.
In the example below, the three sounds have been broken into 12 separate parts.
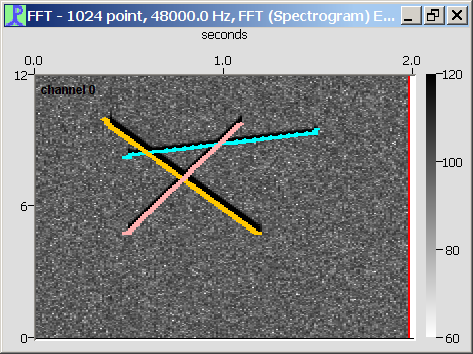
Re-link across joins
If this option is selected, then the algorithm will attempt to rejoin individual tones across joins. First, the sound is broken up as above, it then rejoins the different components according to the following rules:
If there are the same number of sounds in consecutive time slices and each sound in the earlier slice is in contact with one in the later slice, then they are joined with 1:1 correspondence.
A crossing point is defined as a sound which has the same number of other sounds entering it as leave it and has a total length no longer than the set maximum in the options dialog. Sounds entering and leaving a cross are linked across it with the highest frequency sound on one side joining the lowest frequency sound on the other.
If there is a branch (one sound splitting to two or more) or a join (two or more sounds merging into one), then the frequency gradient of the merged part is compared to that of the sounds entering or leaving and the sound with the best match is joined to the merged section. Very short sections (fewer than 10 time slices) are penalised during the comparison to favour longer whistles.
Which branching and joining method you chose may depend on the application. Generally, re-linking across joins is the best option for small cetacean whistles.