Noise Removal and Thresholding
Noise removal and thresholding is one of the most important steps in the operation of the Whistle and Moan detector.
Noise removal and thresholding is a five stage process. The first stage has to occur before FFT data are calculated in the FFT (Spectrogram) Engine. The remaining four stages can take place either in the FFT (Spectrogram) Engine module or in the Whistle and Moan detector.
Performing the noise removal in the FFT (Spectrogram) Engine module has the advantage that other PAMGuard processes and displays will have access to the data
The Whistle and Moan detector will try to ensure that the correct noise removal processes are run once and only once but looking back at the FFT data source and testing whether noise removal has already been done.
Noise removal processes which have already been conducted in an earlier module cannot be repeated. However, the Whistle and Moan detector cannot check, and has no control over the configuration of noise removal processes conducted in earlier modules.
Generally, you should use the default settings
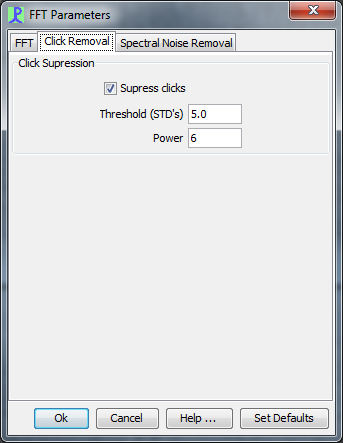
Click Removal
Median Filter
Average Subtraction
Gaussian Kernel Smoothing
Thresholding
Click Removal
This stage of the noise removal has to take place on the raw data prior to the calculation of the spectrogram. It is therefore carried out by the FFT (Spectrogram) Engine.
The click removal method operates on the time series data prior to the FFT calculation and therefore affects both output streams of the FFT Engine.
Click removal measures the standard deviation of the time series data and then multiplies the signal by a factor which increases rapidly for large signal components. This has the effect of reducing the magnitude of short duration transient signals such as echolocation clicks
Other noise removal stages can be controlled from either the Whistle and Moan detector dialog or from the FFT (Spectrogram) Engine
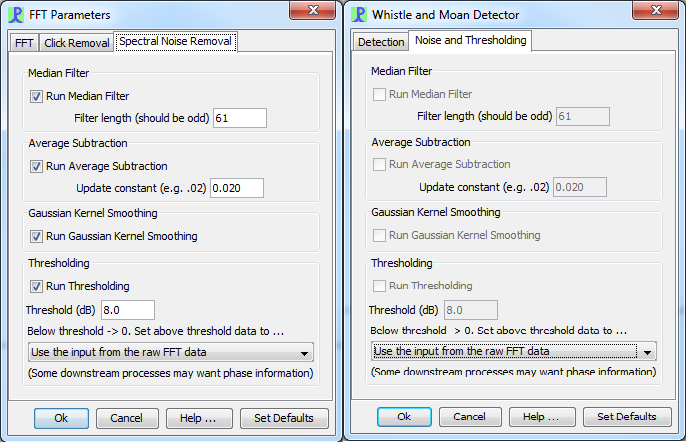
Median Filter
Within each spectrogram slice, the median value about each point is taken and subtracted from that point.
Average Subtraction
A decaying average spectrogram is computed and subtracted from the current spectrogram value.
Gaussian Kernel Smoothing
The spectrogram is smoothed by convolving the image with a Gaussian smoothing kernel
1 2 1
2 4 2
1 2 1.
Thresholding
A threshold is applied and all data falling below that threshold set to 0.
Although the Connected Region Search uses only a binary map of parts of the spectrogram which are above or below threshold it is generally more useful to output the input from the raw FFT data which will have been multiplied by the binary map. This will contain phase and amplitude information which can be used by the Whistle and Moan detector for measuring time delays between channels and the overall whistle amplitude.